

Configuring external (USB) floppy drive on openSUSE Linux
Connect USB floppy drive to PC; no floppy inside. There shouldn’t be any other USB memory devices connected.
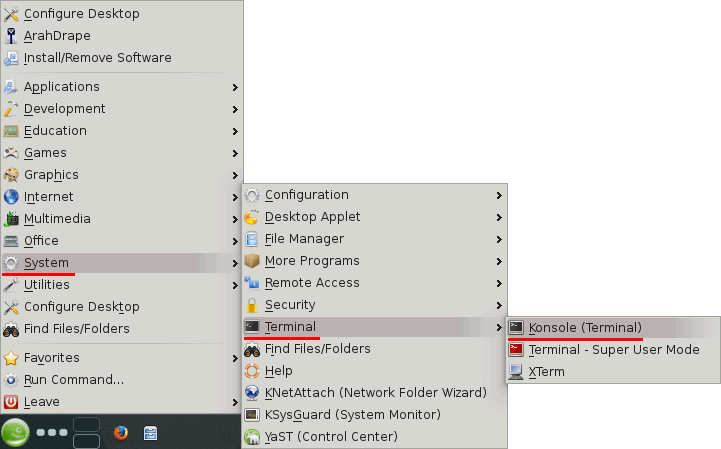
First, you need to find, which device name is used in your system for the USB floppy drive. Open a terminal window (Suse menu (green icon) > Sytem > Terminal > Konsole (Terminal).
In the terminal type following command (press the Enter key after it):
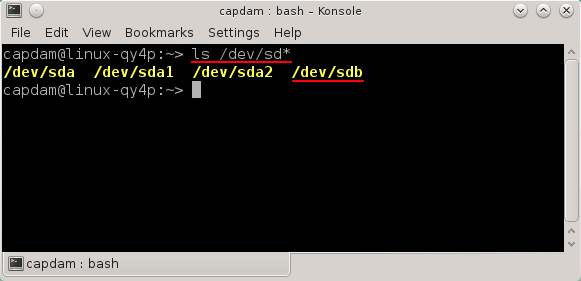
ls /dev/sd*
The output of the command is the device list. You can distinguish the USB floppy drive from the hard drive(s) quite easily: the USB floppy drive is usually listed as a last device, and it does not contains partitions, which are represented as numbers on the end of the names.
On the image below, the floppy drive is labeled as /dev/sdb
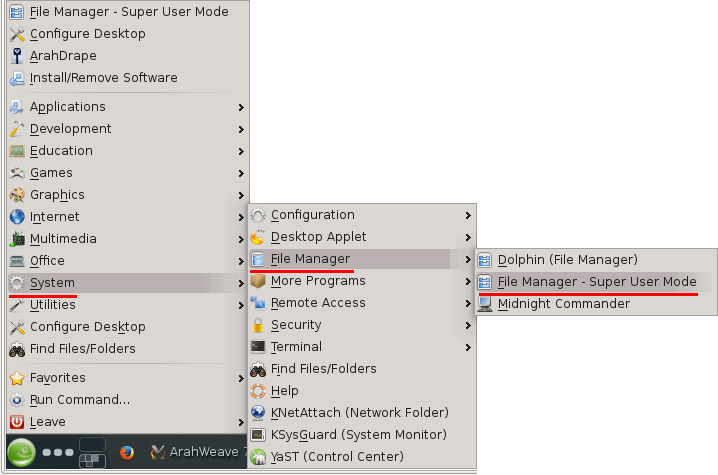
Then go to Suse menu (green icon) > System > File manager > File manager -Super user mode
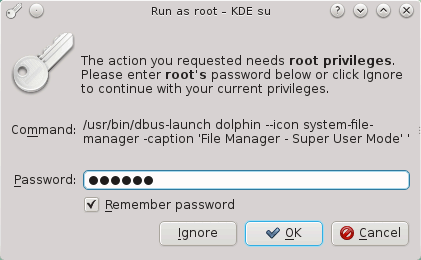
Enter the administrator (root) password.
In the file manager, navigate to /etc/init.d, and click with right mouse button on the boot.local file icon. Choose Open with > Kwrite.
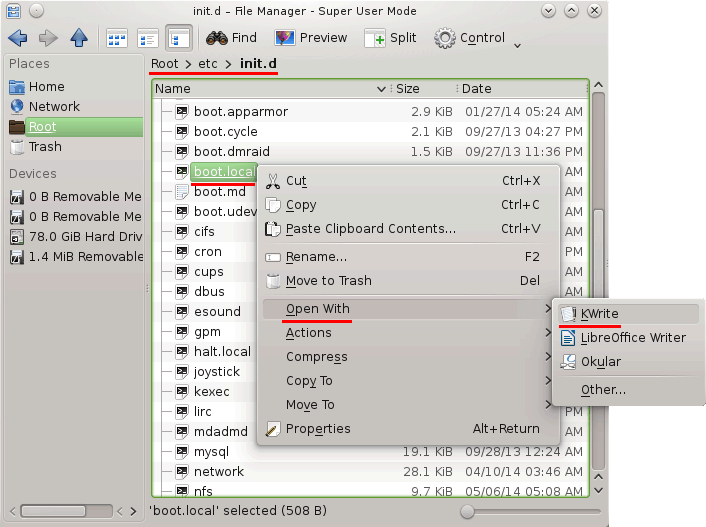
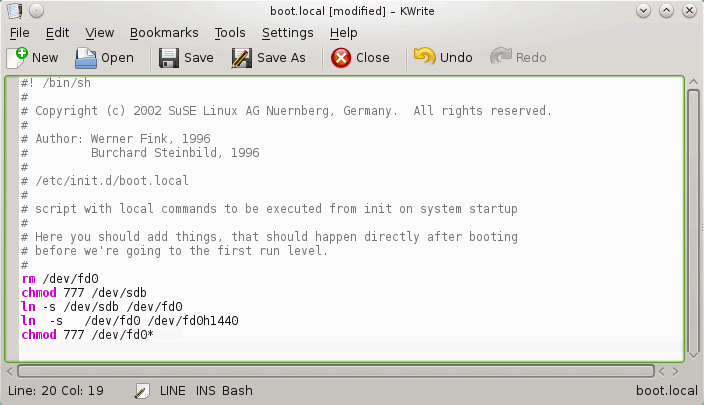
Add the following lines at the end of a file (we use /dev/sdb as a device name in the commands below. You should use the device name according to the output of ls /dev/sd* command on your system.):
rm /dev/fd0
chmod 777 /dev/sdb
ln -s /dev/sdb /dev/fd0
ln -s /dev/fd0 /dev/fd0h1440
chmod 777 /dev/fd0*
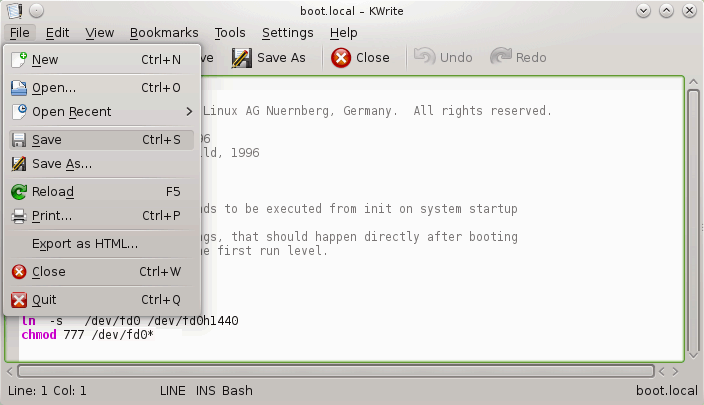
Save the file (File > Save), and close KWrite editor.
Restart computer. If you will leave the USB floppy drive plugged in all the time, it will alwasy use the same device label, so you won’t need to modify the boot.local file again.